Ted Talk 3d Printing Organs
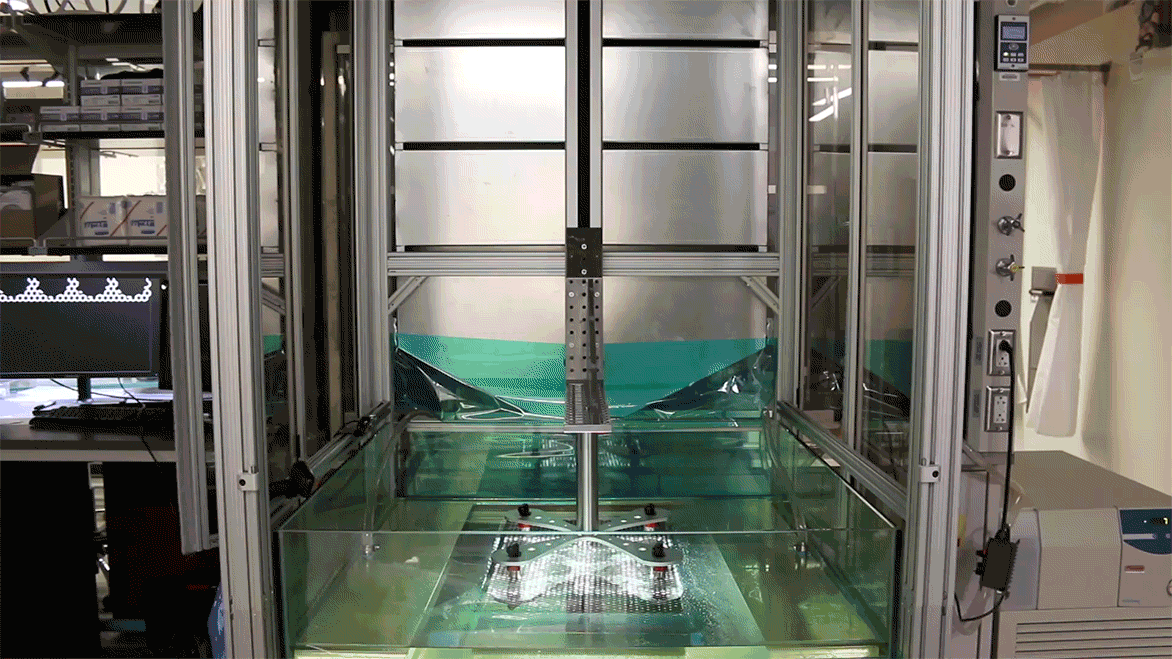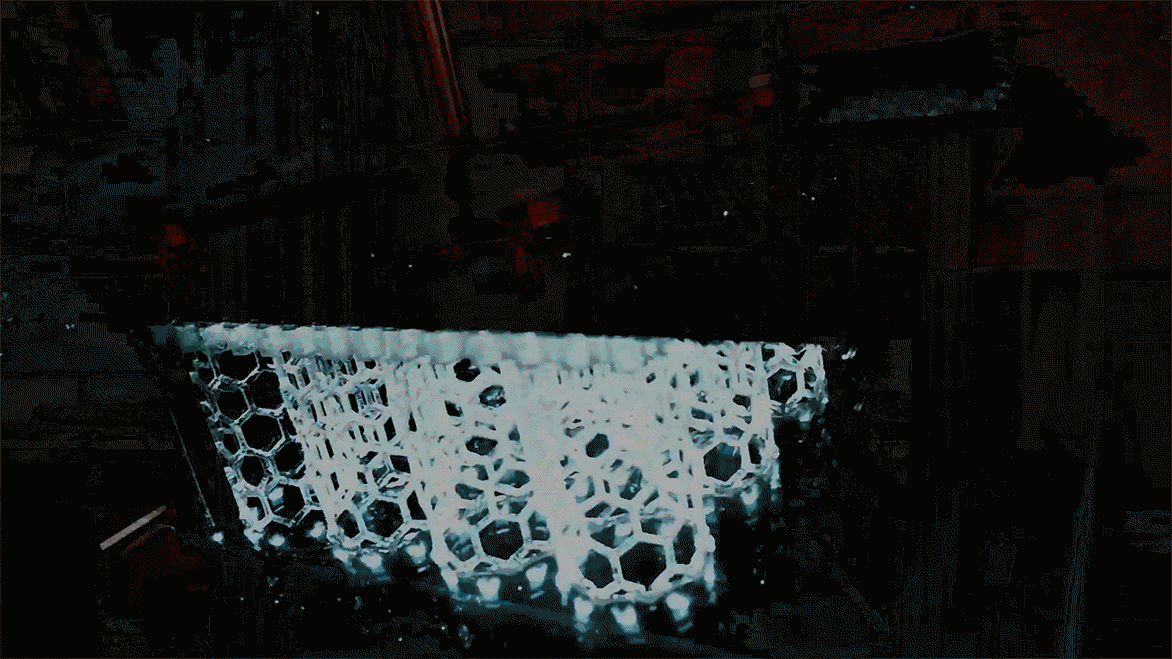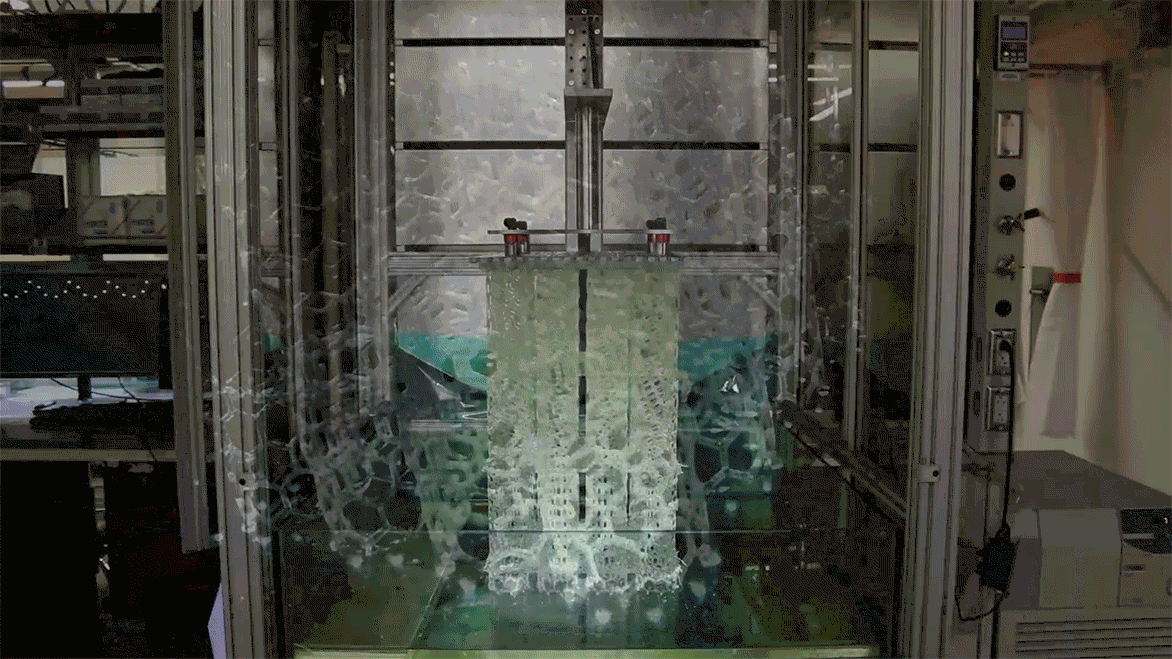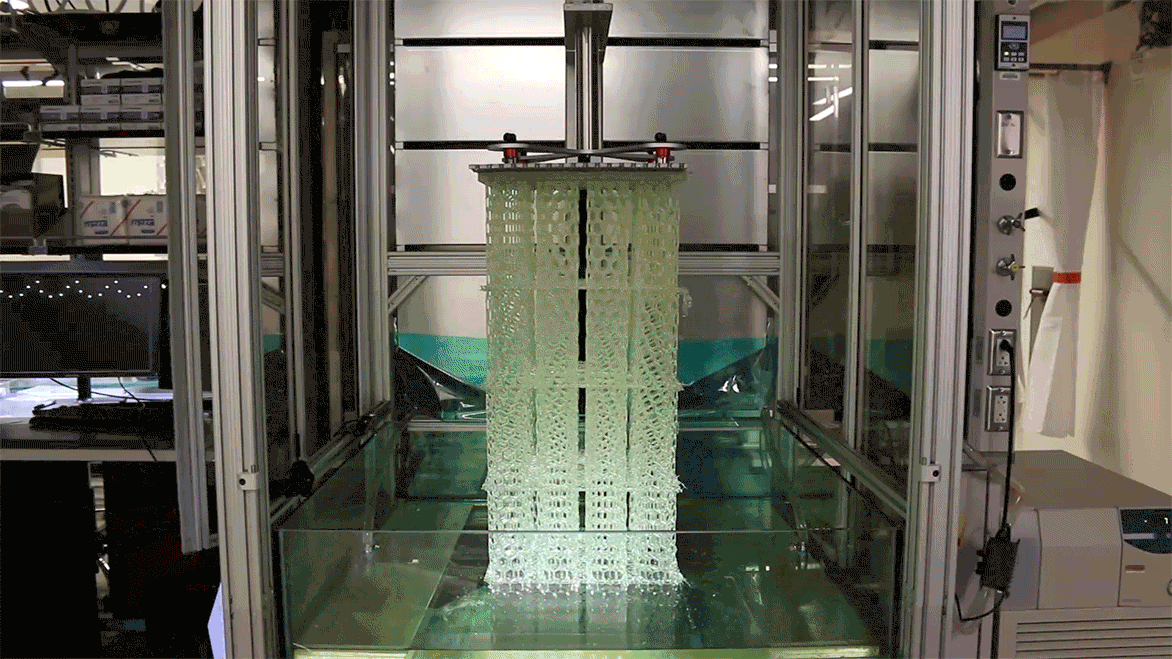
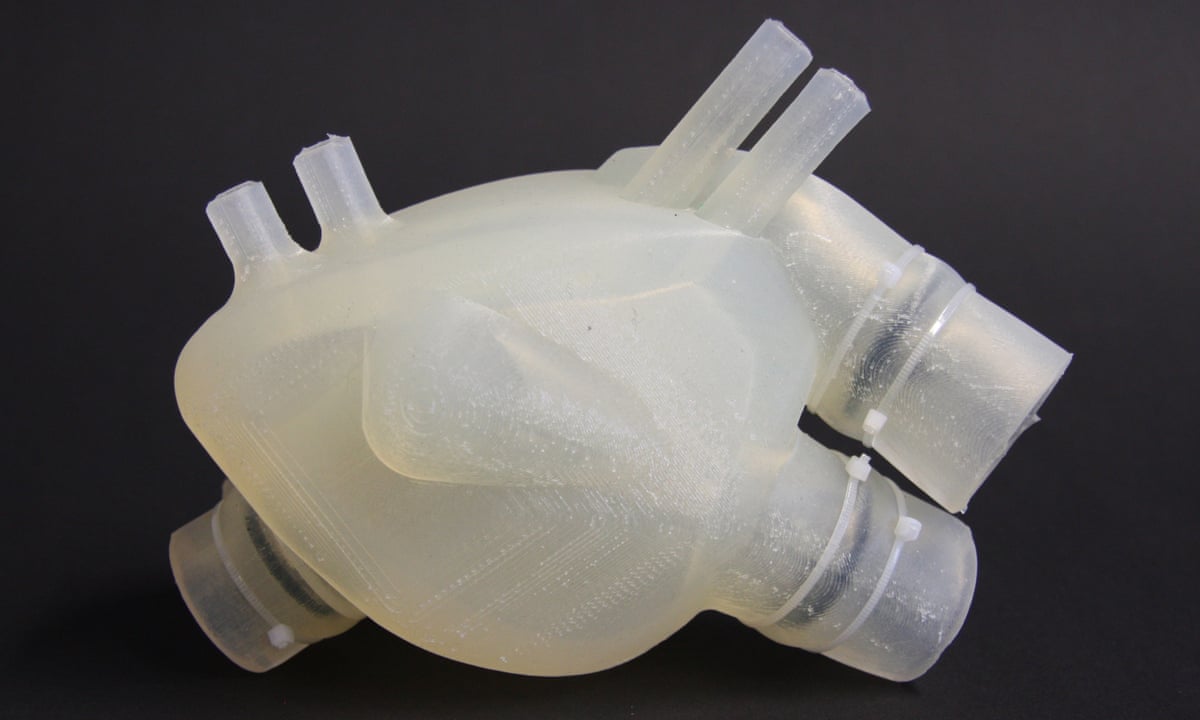
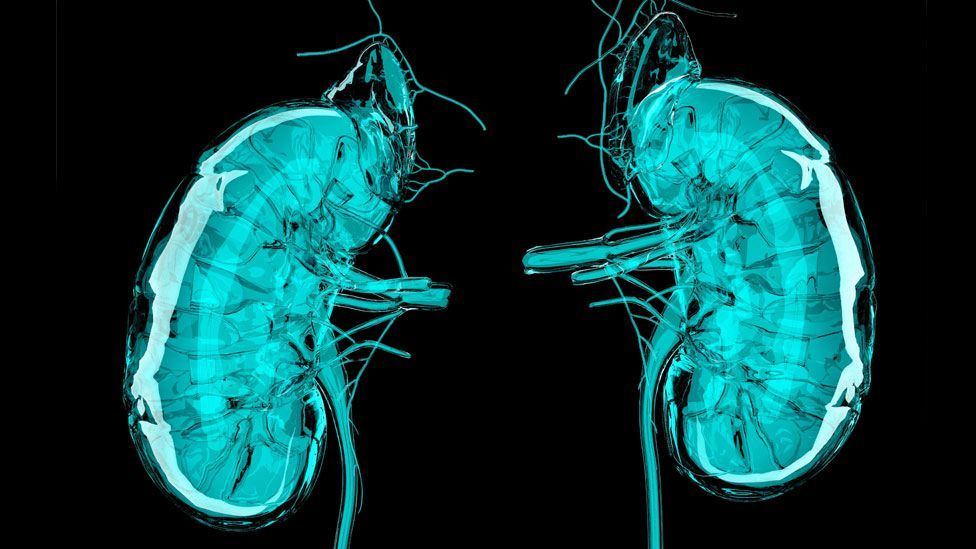
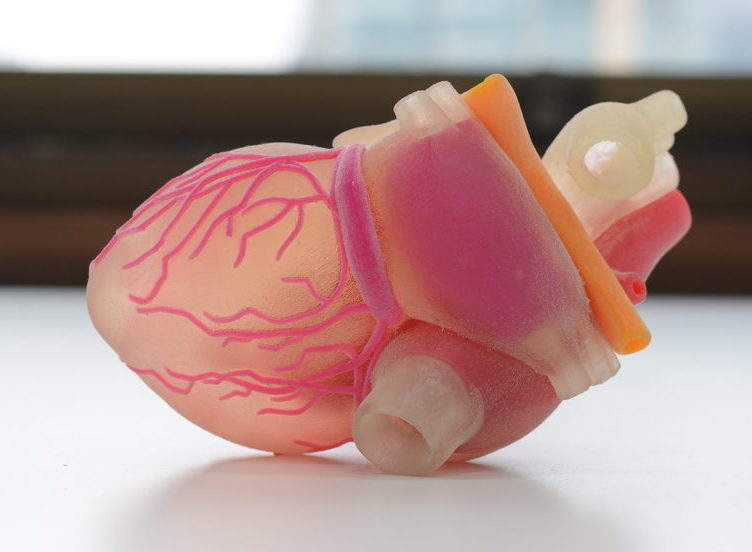
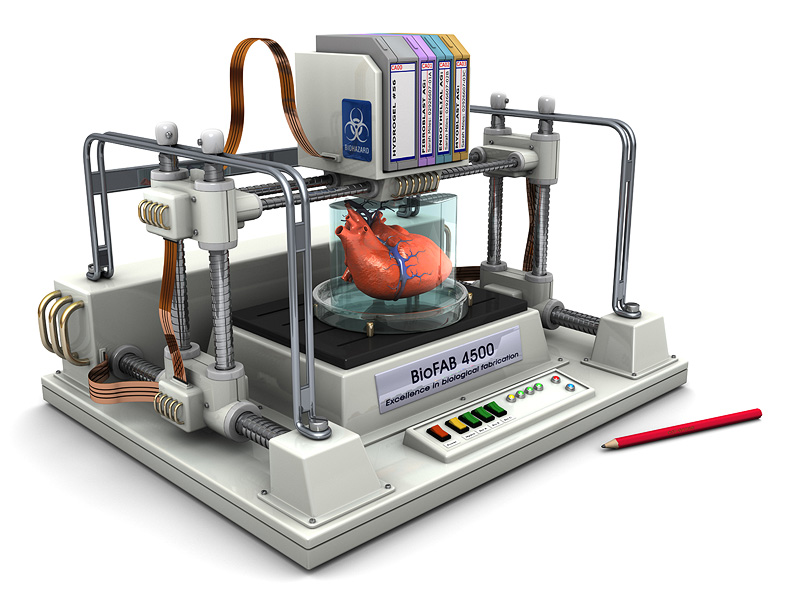
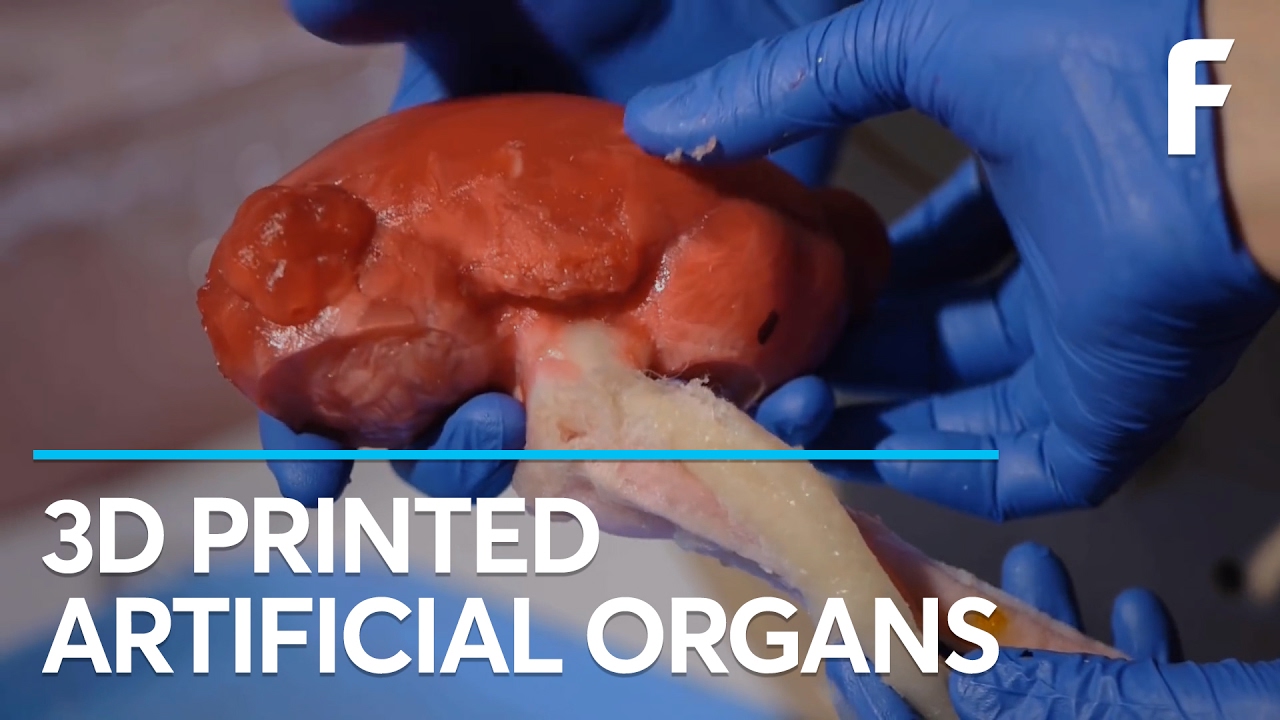
A 3d printer that uses living cells to output a transplantable kidney.

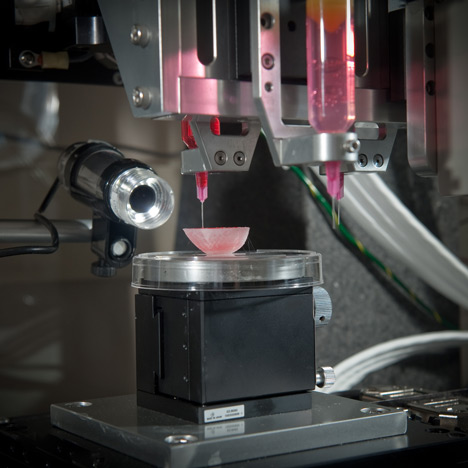
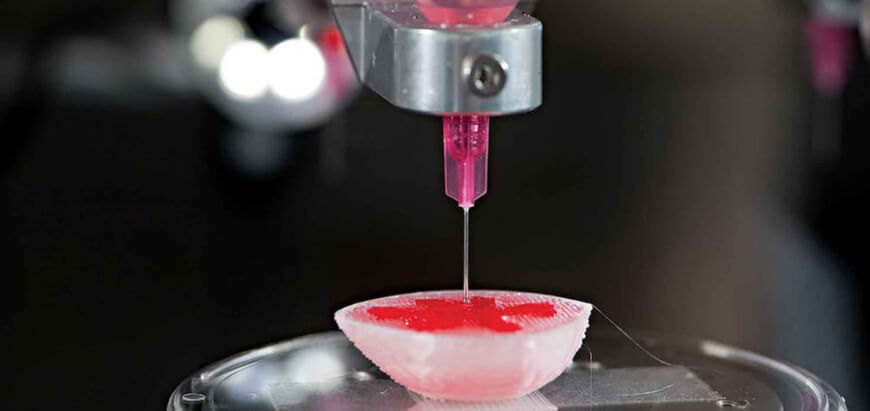
Ted talk 3d printing organs. Scientists and engineers utilize 3d bioprinting for several applications. A big reason behind. A printable material that contains living cells. Instead of starting with metal plastic or ceramic a 3 d printer for organs and tissues uses bioink.
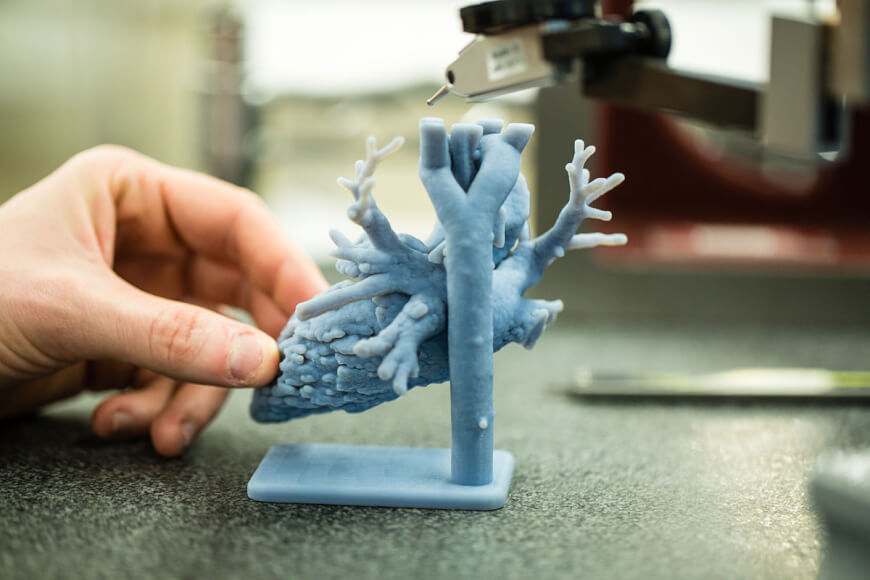
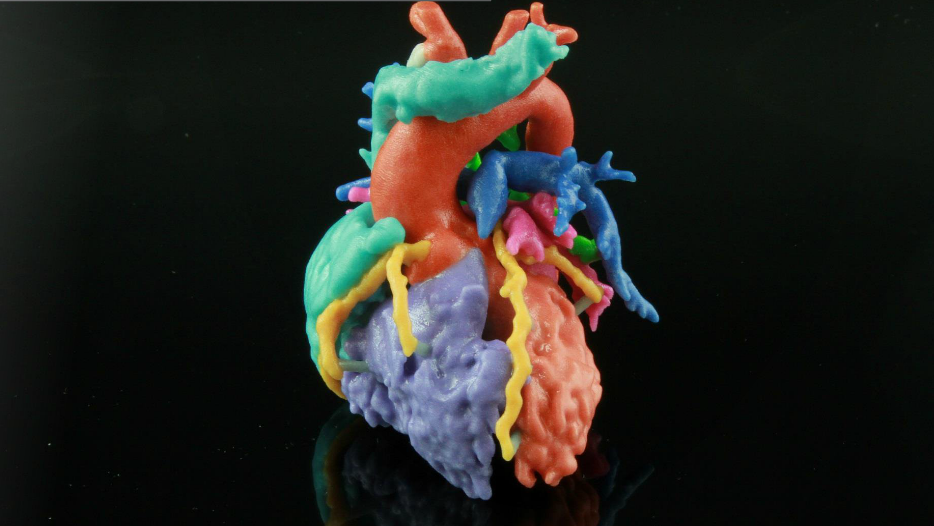
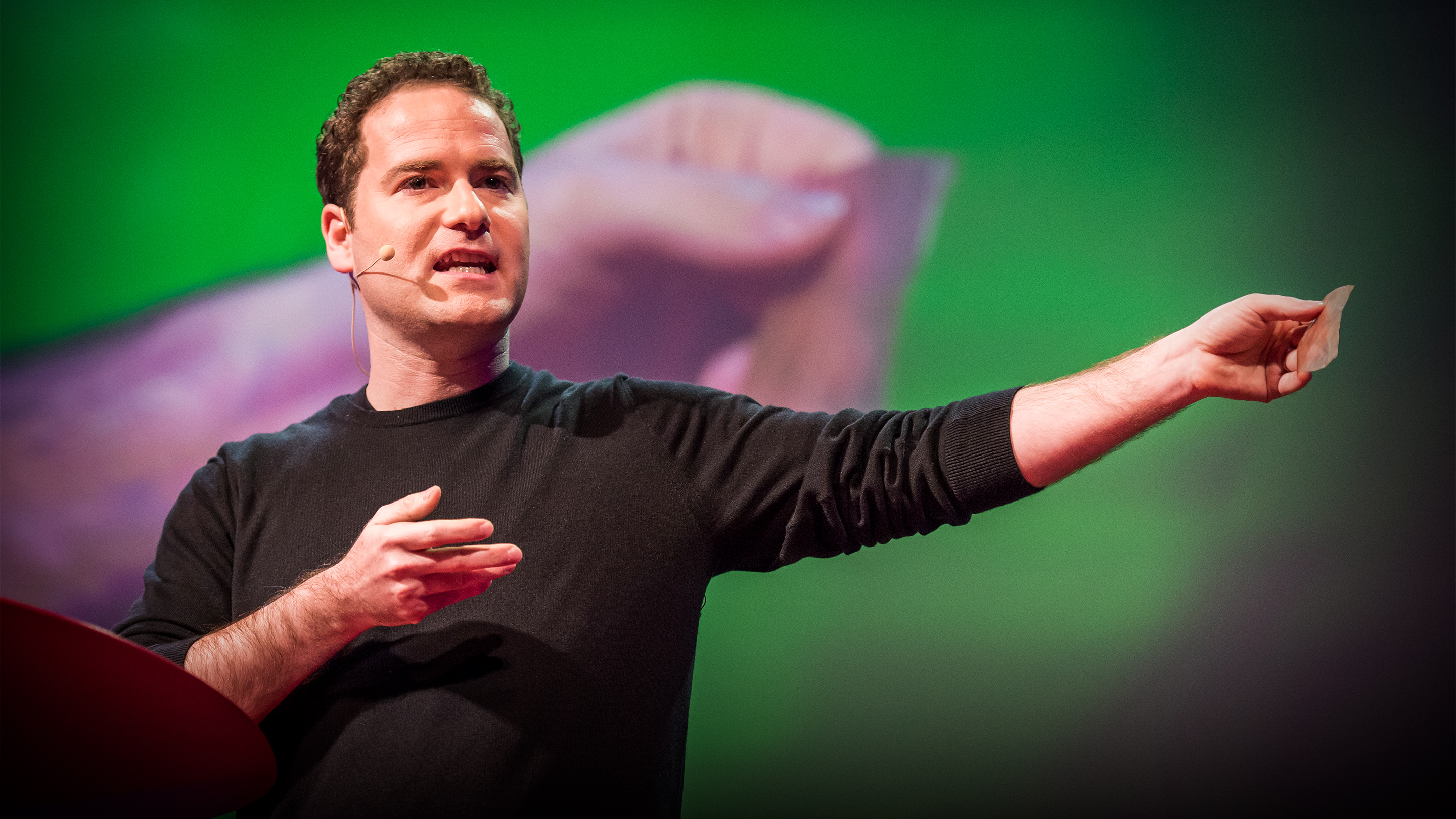
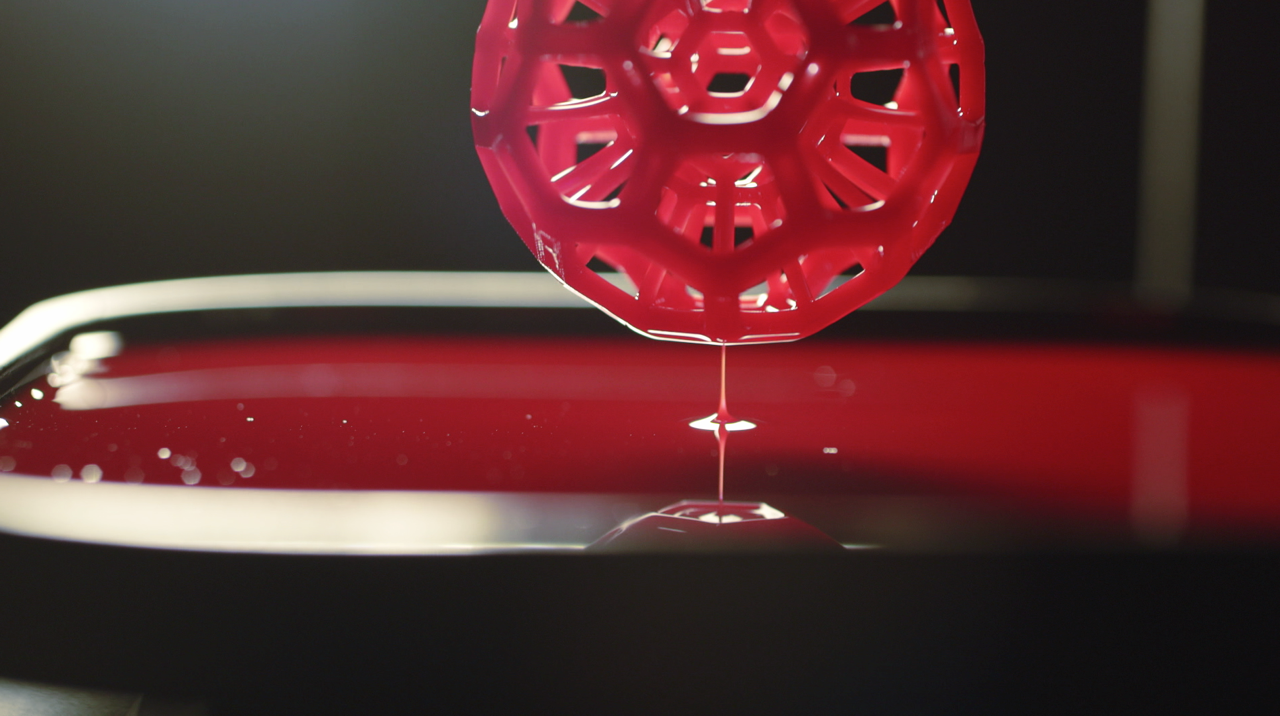
This video was produced by tedmed. Surgeon anthony atala demonstrates an early stage experiment that could someday solve the organ donor problem. Organs have been successfully transplanted from either cadavers or living donors but the demand for an organ exceeds the current availability. What if you could 3d print a human organ.
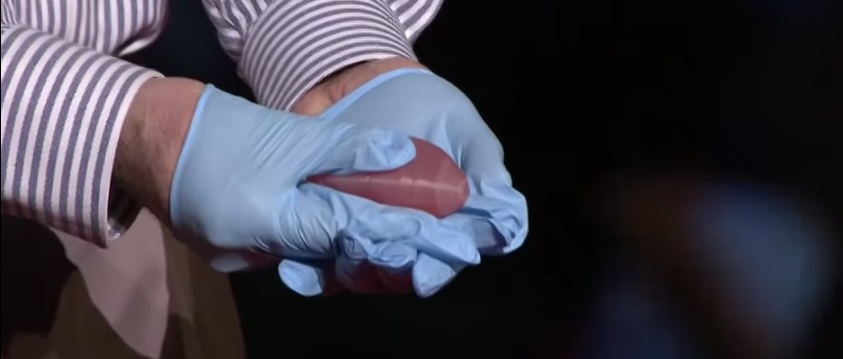
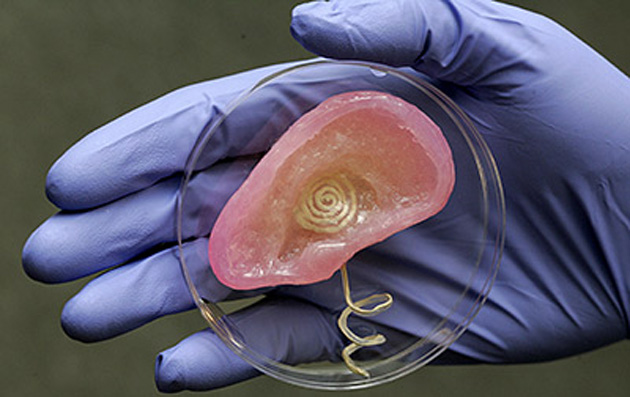
At tedmed he shows footage of his bio engineers working with some of its sci fi gizmos including an oven like bioreactor preheat to 986 f and a machine that prints human tissue. But the aftermath w. Atalas young patient luke massella received an engineered bladder 10 years ago. A record amount of money is spent developing new drugs but drug approval rates are declining and many fatal diseases are left untreated.
One use of 3d bioprinting. The bulk of many bioinks are water rich molecules called hydrogels. The company has its rd based in paris and its sales based in boston. The shortage of organ donations is a crisis in healthcare.
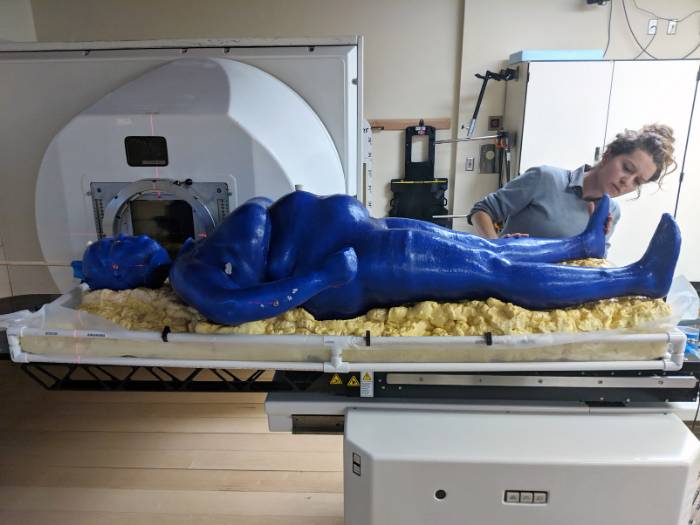
Their goal is to develop copies of patient organs organ twins using 3d printing allowing the surgeons to train prior to. Ted talk lets begin surgeon anthony atala demonstrates an early stage experiment that could someday solve the organ donor problem. Using similar technology dr. Mixed into those are millions of living cells as well as various chemicals that encourage cells to communicate and grow.
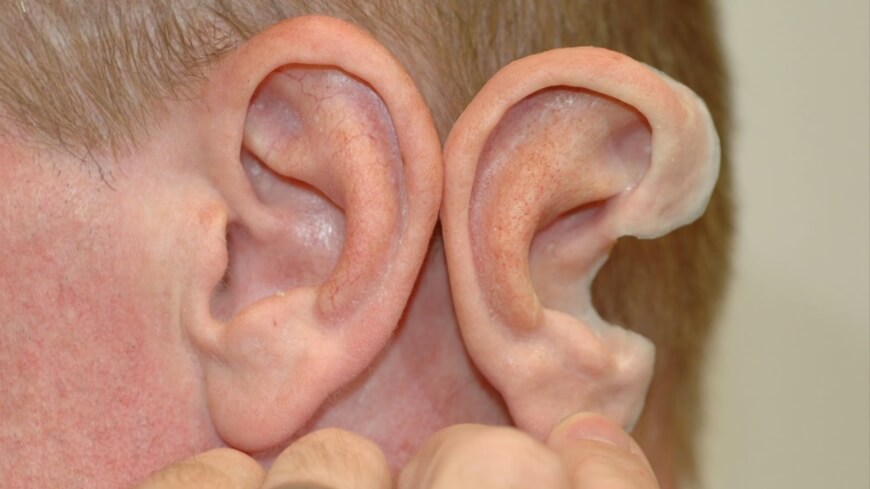
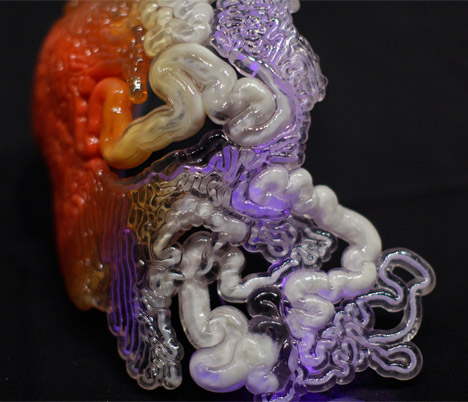
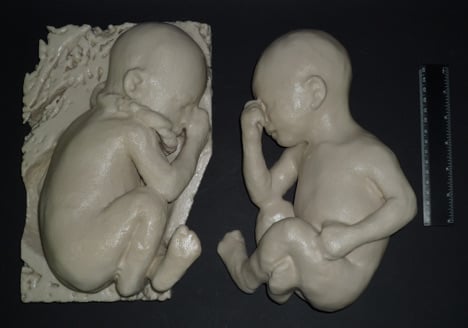
Losing a limb was an all too common fact in the civil war torn region. Anthony atalas state of the art lab grows human organs from muscles to blood vessels to bladders and more. We meet him onstage.

































































/https://public-media.si-cdn.com/filer/09/43/0943f676-f58a-450d-9a71-9dfa30bd961d/may2015_a07_bioengineeredorgans.jpg)